Overview of Tight Junctions
Definition: Tight junctions are specialized connections between epithelial or endothelial cells that regulate paracellular permeability and maintain cell polarity.
Functions:
Barrier to solute and water flow.
Fence between apical and basolateral membrane domains.
Signaling hubs regulating cell proliferation and differentiation.
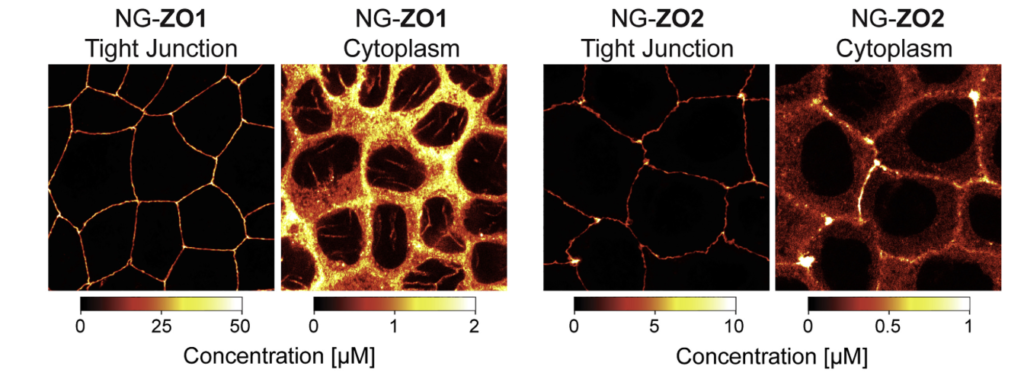
Re-formation of Tight Junctions after Calcium Depletion; Endogenous NG-ZO1 in a Confluent MDCK-II Monolayer. Cell Press, Karina et al., 2019
Scaffolding & Cytoplasmic Proteins
These link transmembrane proteins to the cytoskeleton and signaling machinery.
🧩 ZO-1 (Zonula Occludens-1)
Role: Central scaffolding protein that links claudins and occludin to the actin cytoskeleton.
Domains: Contains PDZ, SH3, and GUK domains for protein-protein interactions.
🧩 ZO-2 and ZO-3
Similar to: ZO-1
Function: Redundant and overlapping roles in junction assembly and maintenance.
🧩 Afadin
Connects: Tight junctions and adherens junctions.
Function: Regulates polarity and junctional integrity.
🧩 Cingulin
Role: Binds actomyosin cytoskeleton and regulates RhoA signaling.
Location: Cytoplasmic plaque of tight junctions.